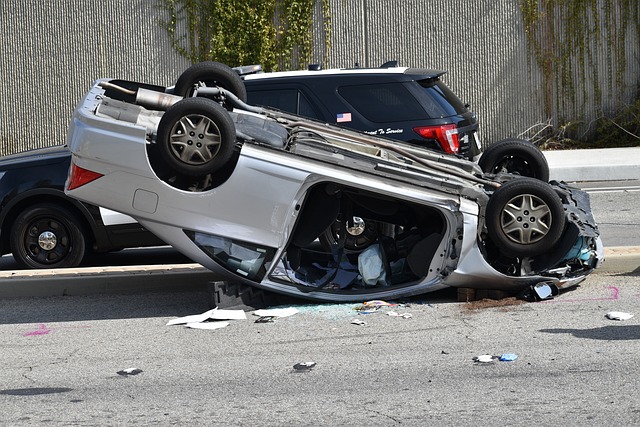
Hazard insurance, crucial for homeowners, protects properties from natural disasters and unforeseen events. Borrowers must assess local risks, as policies vary by location. Coverage includes replacement costs and liability protection, with specialized plans for high-risk areas. Understanding policy details, exclusions, and add-ons like loss of use coverage is essential. Efficient claims processes ensure swift recovery, emphasizing clear communication and documentation. Hazard insurance is a vital shield, offering peace of mind and financial security for real estate investments.
In the complex landscape of real estate transactions, understanding hazard insurance is a pivotal step for buyers seeking to protect their investment. This essential coverage plays a crucial role in mitigating financial risks associated with unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or property damage. However, navigating the intricacies of various policies and terms can be daunting. This article provides an actionable resource explaining hazard insurance in clear, concise terms tailored for real estate buyers. By demystifying this critical aspect of homeownership, we empower individuals to make informed decisions and safeguard their financial future with confidence.
Understanding Hazard Insurance: Basics Explained
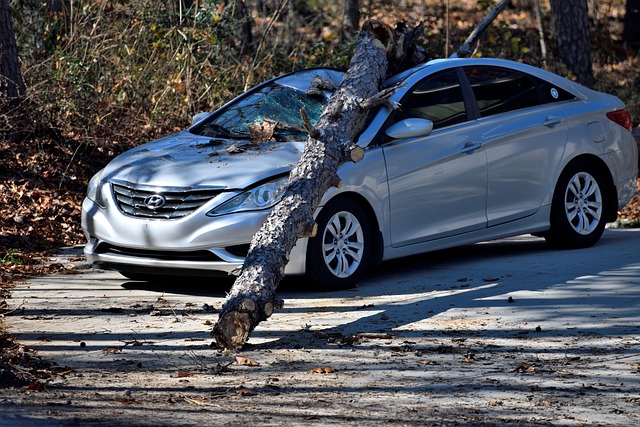

Hazard insurance is a crucial aspect of homeownership, offering protection against unforeseen events that could lead to significant financial losses. At its core, hazard insurance, often referred to as homeowners’ insurance, is designed to safeguard both the physical structure of a property and valuable belongings inside. This type of insurance policy acts as a shield, covering costs associated with damage or destruction caused by specific hazards. Understanding hazard insurance involves grasping its basic principles, coverage options, and how it becomes a vital component in a borrower’s financial strategy.
When considering hazard insurance, borrowers need to be aware of the potential risks unique to their region. These hazards can include natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires, each carrying distinct challenges. For instance, homeowners in areas prone to flooding may require separate flood insurance beyond their standard hazard policy. Data from recent years has highlighted the increasing frequency and severity of these events, making hazard insurance borrower requirements more stringent. Lenders typically mandate adequate coverage to protect both the property and their investment.
The primary objective of hazard insurance is to provide financial peace of mind by mitigating the impact of unforeseen disasters. Policies offer replacement cost coverage for damaged or destroyed property, ensuring homeowners can rebuild or replace assets without facing substantial out-of-pocket expenses. Additionally, personal belongings are protected, offering compensation for their value in case of theft, damage, or destruction. Borrowers should carefully review policy details to understand exclusions and limitations, ensuring they align with their specific needs. Regularly updating coverage amounts is essential as property values change over time, especially for borrowers who have invested in substantial improvements.
Why You Need It: Identifying Potential Hazards

Hazard insurance is a crucial component of home ownership that often gets overlooked until it’s too late. Understanding potential hazards inherent in any property—from natural disasters like floods or earthquakes to more mundane issues such as fire or water damage—is essential for any buyer. Identifying these risks upfront allows borrowers to make informed decisions and ensure adequate protection through the right hazard insurance policies, a requirement for most mortgage lenders.
Every location presents unique challenges. For instance, home buyers in flood-prone areas may face significantly higher premiums due to the heightened risk of water damage. Similarly, earthquake zones demand specialized coverage. According to recent data, over 50% of natural disasters globally are now related to climate change, making hazard insurance even more critical. This includes extreme weather events like hurricanes and wildfires, which can devastate homes and leave owners with substantial repair bills or even total loss.
To prepare, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of potential hazards specific to their area. Local authorities often provide resources on high-risk zones for floods, wildfires, earthquakes, and other disasters. This proactive step ensures borrowers understand not only the need for hazard insurance but also the specific types of coverage required by their lender and tailored to their property’s unique vulnerabilities. By addressing these concerns, buyers can mitigate financial risks and secure a safety net against unforeseen events, ensuring peace of mind in their new home.
Types of Coverage: Protecting Your Investment
Hazard insurance is a crucial component of protecting your investment when purchasing real estate. Understanding the different types of coverage available allows borrowers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. This section delves into the protective measures that extend beyond traditional home ownership, ensuring assets are safeguarded against unforeseen circumstances.
One key aspect to consider under hazard insurance is comprehensive coverage for physical damages. Policies typically cover perils like fire, lightning, windstorms, hail, and even some types of flooding. For instance, a borrower in a region prone to hurricanes would benefit from this coverage, ensuring their investment is secured against potential storm damage. According to recent data, properties with adequate hazard insurance face shorter recovery times and incur less financial burden post-disaster.
Additionally, hazard insurance often includes liability protection, shielding borrowers from claims of bodily injury or property damage incurred by others on their insured premises. This is particularly relevant for buyers who plan to rent out part or all of their property. For example, if a tenant slips and falls on wet flooring, the borrower’s liability coverage can help manage legal costs and potential damages awarded. It’s essential to review policy details, as exclusions and limitations vary, ensuring borrowers understand what’s covered and what’s not under their hazard insurance borrower requirements.
Extending beyond physical damages and liability, certain policies offer additional protections like loss of use coverage, which compensates for income loss if the insured property becomes uninhabitable. This can be invaluable for homeowners who rely on their properties as primary residences or investment sources. By understanding these various coverage options, borrowers are empowered to choose a hazard insurance policy that aligns with their goals and mitigates potential risks, safeguarding their real estate investments comprehensively.
Buying Guide: Key Considerations for Policyholders

When considering a purchase of a new home or investment property, understanding your hazard insurance options is crucial. Hazard insurance isn’t just another box to check; it’s a protective shield safeguarding your financial well-being against unforeseen events. As every property faces unique risks – from natural disasters like floods and earthquakes to perils like fire and vandalism – a tailored hazard insurance policy ensures you’re prepared for the unpredictable.
For borrowers, especially first-time buyers, navigating this process can be daunting. A key consideration is recognizing that standard homeowner’s policies often exclude certain hazards, such as flooding or seismic activity, requiring separate coverage. This is where thorough research and consultation with experts comes into play. Lenders typically require adequate hazard insurance to protect their investment, and borrowers should proactively engage in this process. One practical step is evaluating your property’s location and history. Are there known flood zones? Has the area experienced recent volcanic activity? Such insights guide you in selecting the appropriate coverage – whether it’s a standard policy or a specialized one catering to specific hazards.
Moreover, understanding the fine print is essential. Policyholders should scrutinize deductibles, coverage limits, and exclusions. For instance, while a low deductible may seem appealing initially, it could lead to out-of-pocket expenses during a claim. Conversely, ample coverage ensures financial protection in case of significant damage or loss. As a rule of thumb, borrowers should aim for policies that offer comprehensive protection tailored to their property’s unique hazard profile. This proactive approach not only fulfills borrower requirements but also provides peace of mind knowing your investment is shielded from the unexpected.
Claims Process: What to Expect and How to Navigate

The claims process is a critical aspect of hazard insurance, serving as the bridge between an insured event and financial compensation. It’s a structured procedure designed to ensure fairness, promptness, and accuracy in settling losses. Understanding this process beforehand empowers buyers, enabling them to navigate potential challenges effectively.
When a covered hazard occurs, such as property damage from a natural disaster or theft, the borrower initiates the claims process by notifying their insurance provider. This typically involves filing a detailed report, providing evidence, and supplying relevant documentation like police reports or repair estimates. Once received, the insurer assigns a claims adjuster to review the information. The adjuster assesses the damage, verifies coverage, and calculates the claim amount based on policy terms and local market values. This step is crucial as it determines the extent of financial assistance.
Effective communication between borrowers and insurers during this phase cannot be overstated. Borrowers should actively engage with adjusters, asking questions about the process, expected timelines, and their rights. It’s also beneficial to document interactions, keeping records of conversations and decisions made. For instance, in cases of significant damage, borrowers might need to arrange temporary housing or make emergency repairs while awaiting insurance settlement. Being prepared for these eventualities can alleviate stress and ensure a smoother claims experience.
Knowing their hazard insurance borrower requirements is paramount for buyers. These requirements dictate the information needed to process claims efficiently. For example, some policies may mandate specific reporting deadlines, documentation types, or even require borrowers to mitigate damages promptly. Adhering to these requirements ensures that claims are settled without delay and maximizes the available coverage benefits.
